“SAP and users were best friends – and then came the cloud.” This quote aptly illustrates that some companies are currently taking a critical view of SAP’s path and offerings. Yet many of our customers are facing enormous challenges.
1. the four most important ones in my perception are: Many companies’ own IT landscapes are often complex and only able to cope with new challenges to a limited extent. Traditional systems are often cumbersome and inflexible, making it difficult to adapt to new business requirements. These systems were designed and structured for a different era when business conditions and requirements were different.
2. the increased networking of business processes and devices increases vulnerability to cyberattacks. At the same time, regulatory requirements are increasing, particularly with regard to data protection. This presents companies with the challenge of designing their systems and processes in such a way that they are both secure and compliant.

3. New technologies come onto the market every day. These are often quickly adopted by competitors, increasing the pressure on companies to keep up. The cloud offers the opportunity to implement these new technologies faster and more efficiently, but this requires careful planning and implementation to avoid getting caught up in the spider web of dependencies.

4. Finally, the new business models made possible by digitalization pose challenges for the entire organization. The cloud can help to support these new models, but this requires a change in mindset and often also in organizational structure. Overall, migrating to the cloud is a complex task that needs to be carefully planned and implemented.

Good decisions start with good questions. The answers to good questions are almost always found in data. In our increasingly digitalized world, the ability to collect, analyze, and gain insights from this data is critical. Analytics plays a central role in digital transformation as it enables companies to make data-driven decisions that lead to better business outcomes. Furthermore, today’s business world requires more than ever that all employees, regardless of their role or position, be able to use data effectively. This enables them to find innovative solutions, improve processes, reduce costs, and open up new opportunities. I see four key areas for the further development of analytical skills:
- Data Decentralization: data decentralization is about distributing and managing data across different areas and platforms. This can improve data accessibility and utilization but also requires tight control and management to ensure data consistency and security. The challenge is to find the right balance between decentralization and control.
- Trustworthy data: Data is only as good as its quality and reliability. Ensuring that the data we use is accurate, up-to-date, and complete is a major challenge. This requires robust data quality management practices and often the implementation of data cleansing and validation technologies.
- Data empowerment: Data empowerment refers to the ability of all employees in an organization to access and use data for their work. One challenge is to provide the necessary training and resources to enable all team members to use data effectively. At the same time, the company must comply with data protection regulations and ensure that sensitive data is protected.
- Data innovation: With the rapid evolution of technologies and analytics, it is a constant challenge to stay up-to-date and find innovative ways to utilize data. This may involve implementing artificial intelligence, machine learning, or advanced data visualization techniques. It requires an ongoing investment in technology and expertise as well as a culture of openness to experimentation and change.
Is SAP (still) the right partner for the new challenges?
To overcome these challenges, it is crucial that companies have a clear data strategy that is supported by senior management. In addition, it’s important to continually invest in data management skills and technologies and foster a data-driven culture throughout the organization.
In short, harnessing the power of analytics isn’t just desirable – it’s absolutely necessary for any organization that wants to succeed in the modern business world.
Last week’s DSAG annual conference was an important meeting place for SAP user companies in the German-speaking world. However, customers expressed their dissatisfaction with the product strategy. One frequently mentioned concern is that they do not want to be forced into the cloud. They believe that the costs involved in carrying out the necessary migration steps are too high.
The use of cloud products is currently often causing difficulties for users. On the one hand, the further development of products is not progressing fast enough. On the other hand, updates lead to existing applications being “destroyed” or having to be constantly migrated. This raises questions about the stability and reliability of cloud solutions and requires careful consideration of the long-term strategy for digital transformation.
But where do we stand with the current products in the SAP Analytics portfolio?
SAP Datasphere is a cloud platform that has been specially developed for processing large volumes of data. It enables companies to collect their data from various sources, analyze it, and gain insights from it. For SAP users, this platform is particularly relevant as it enables them to link their SAP data with other data sources and thus obtain a holistic picture of their company. In addition, SAP Datasphere offers the ability to perform real-time analysis, which can be invaluable for companies to respond quickly to changing market conditions.
The SAP Analytics Cloud is a comprehensive cloud product offered as Software-as-a-Service (SaaS) for business intelligence (BI), planning, and predictive analytics. It offers a wide range of functions that help users to analyze and interpret their data effectively.
Among the SAP Analytics Cloud functions are pre-built functions for creating calculated columns, formulas for analysis and planning, scripting formulas and calculations in advanced formula steps as well as pattern-recognizing functions. These functions enable users to simplify their work by only having to define a few parameters to perform complex analyses.
Organizations use SAP Analytics Cloud for a variety of tasks, including analytics and business intelligence, enterprise planning, and composable analytics. It also provides pre-built business content to enable intelligent, data-driven decision-making capability.
Despite the large number of functions and application options, there is still room for improvement. Some users find it difficult to find the operation intuitive. It’s great that new functions are constantly being added to the Analytics Cloud. In my view, customers are demanding more and faster innovations, but please without interruptions. When SAP HANA was introduced, SAP promised “innovation without disruption”.
In my view, the approach of only operating the products as SaaS solutions remains critical. More options for companies would certainly make sense here.
Many analytical requirements can be met with data from a source system. S/4HANA in particular already offers a lot of possibilities here, which I don’t think everyone is taking advantage of yet.
Core Data Services (CDS) views are crucial in the S/4HANA world as they build on existing database tables and views to enable efficient data modeling. They offer a variety of highly effective built-in functions such as SQL operators, aggregations, and expressions to create views. Because the CDS views that make up the Virtual Data Model (VDM) follow consistent modeling and naming rules, they can provide business data in a format that is easy to understand and use.
The power of CDS views is also evident in their ability to enable more advanced and semantically rich data modeling. They are an improvement on the ABAP layer and provide an enhanced and semantically richer data model. This not only improves data processing and query performance but also facilitates data modeling. However, it must be clearly stated that the development of CDS views is not for the business user. This requires a specialist who can deal with all the problems of availability and communication of requirements.
Another advantage of CDS views is the time saved during Fiori app development. Fiori apps are the user interface of SAP S/4HANA. With CDS-Views, developers can quickly and efficiently create customized Fiori apps that are precisely tailored to a company’s requirements and processes.
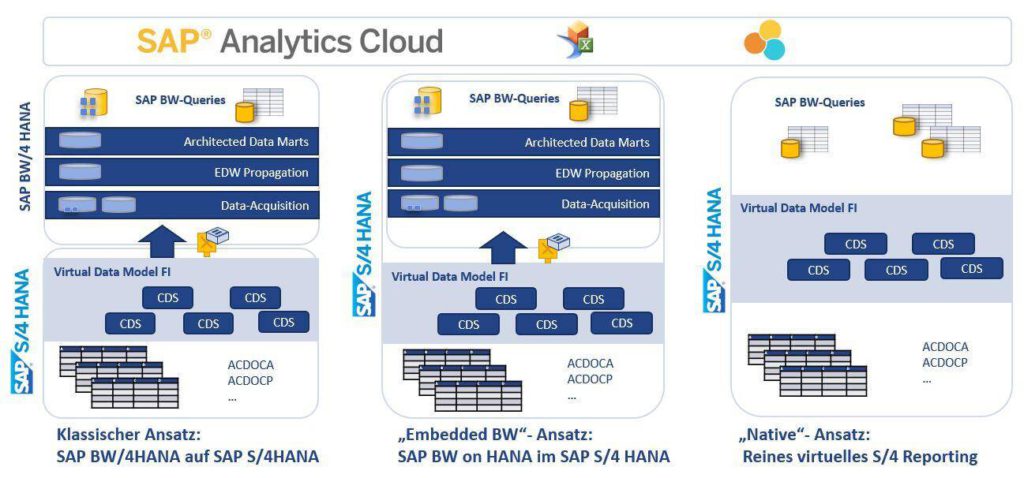
The CDS views also serve as a solid basis for embedded analytics in S/4HANA. They form a modeling layer that serves as a starting point for embedded analytics with CDS queries. This enables companies to analyze their data effectively and gain insights that can help improve business processes.
With the new functions, SAP is strengthening integration within the SAP stack. “Nobody understands SAP as well as SAP does”. This gives good reasons for companies to rely on SAP. At the same time, I see many requirements where the complexity and focus on SAP functions is unnecessary ballast. In my view, this speaks in favor of a hybrid solution. Especially as the further development of products and prices is only partially secured for the future. Technological change and business decisions by SAP are difficult to predict. The trick is to combine a powerful portfolio of different suppliers and technologies into a [business analytics] platform in such a way that different uses (“as if from a single source”) are possible from the user’s perspective. I am concentrating here on AWS, Azure and Pyramids as very dissimilar platforms.
AWS Analytics is a powerful collection of services and tools that help companies collect, process, and analyze data efficiently. Here are seven specific benefits of the AWS solution:
Versatility: AWS offers a wide range of analytics tools for different needs, including Amazon Quicksight for business intelligence, Amazon Redshift for data warehousing, and Amazon Kinesis for real-time streaming data.
Scalability: With AWS, you can scale your analytics capacity as needed. This means you don’t have to pay for unused resources and your infrastructure can keep pace with the growth of your business.
Security: AWS places great emphasis on security and compliance. All data is stored securely in the AWS cloud and can only be accessed by authorized users.
Integration: AWS analytics tools integrate seamlessly with other AWS services, allowing you to take a comprehensive, unified approach to your data management.
Machine learning: Some AWS analytics tools offer built-in machine learning capabilities that allow you to recognize complex patterns and trends in your data.
Cost efficiency: With AWS, you only pay for what you actually use. There are no upfront costs or long-term commitments, making AWS a cost-effective solution for organizations of all sizes.
Global presence: AWS has data centers around the world, which means you can store your data where it makes the most sense for your business and allows quick access to your data from anywhere.
Azure Data Fabric is an integrated collection of big data and analytics services that enable seamless data processing and analysis.
Here are seven specific benefits of the Azure Data Fabric solution:
- Full integration: Azure Data Fabric is fully integrated into the Azure ecosystem, enabling easy connection with other Azure services such as Azure Machine Learning or Azure Synapse Analytics.
- Scalability: Azure Data Fabric can easily scale to handle large volumes of data, making it ideal for organizations with growing data needs.
- Flexibility: Azure Data Fabric allows you to process data in real-time or in batches, depending on your business needs.
- Security: Azure offers robust security measures, including encryption at rest and in transit, to ensure the safety of your data.
- Ease of management: Azure Data Fabric provides a centralized management interface that simplifies the management and monitoring of your data.
- Cost efficiency: Azure Data Fabric uses a pay-as-you-go model, which means you only pay for the resources you actually use.
- Global availability: With Azure, you can store your data in any of Azure’s global data centers, helping you minimize latency and improve performance.
Pyramid
My colleague has just written a blog about Pyramid, which I am happy to recommend here: Pyramid Analytics
CONCLUSION
Overall, the situation for SAP Analytics users is complex and challenging. While analytics plays an important role in the digital transformation of companies, there are still many challenges to overcome. The dissatisfaction of DSAG members with SAP’s product strategy shows that there is room for improvement and that users need better communication and involvement in the decision-making process.
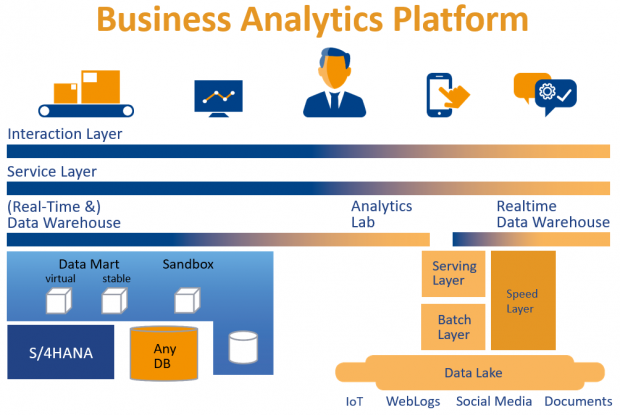
I am convinced that building the Business Analytics Platform for most companies should involve more than just SAP products. Many users face exactly the same challenges, so in my view, it is always worth exchanging ideas …
